2025-06-30
Phosphorus is one of the three essential nutrients for plant growth, playing an irreplaceable role in crop energy metabolism, root development, and flowering/fruiting. Approximately 40% of global arable land suffers from varying degrees of phosphorus deficiency, making proper phosphorus fertilizer application a key measure for increasing agricultural yields.
Phosphorus fertilizers are primarily derived from phosphate rock through processes including crushing, flotation, and acidification. Common varieties include single superphosphate, triple superphosphate, and ammonium phosphates, each with different nutrient contents and application conditions.
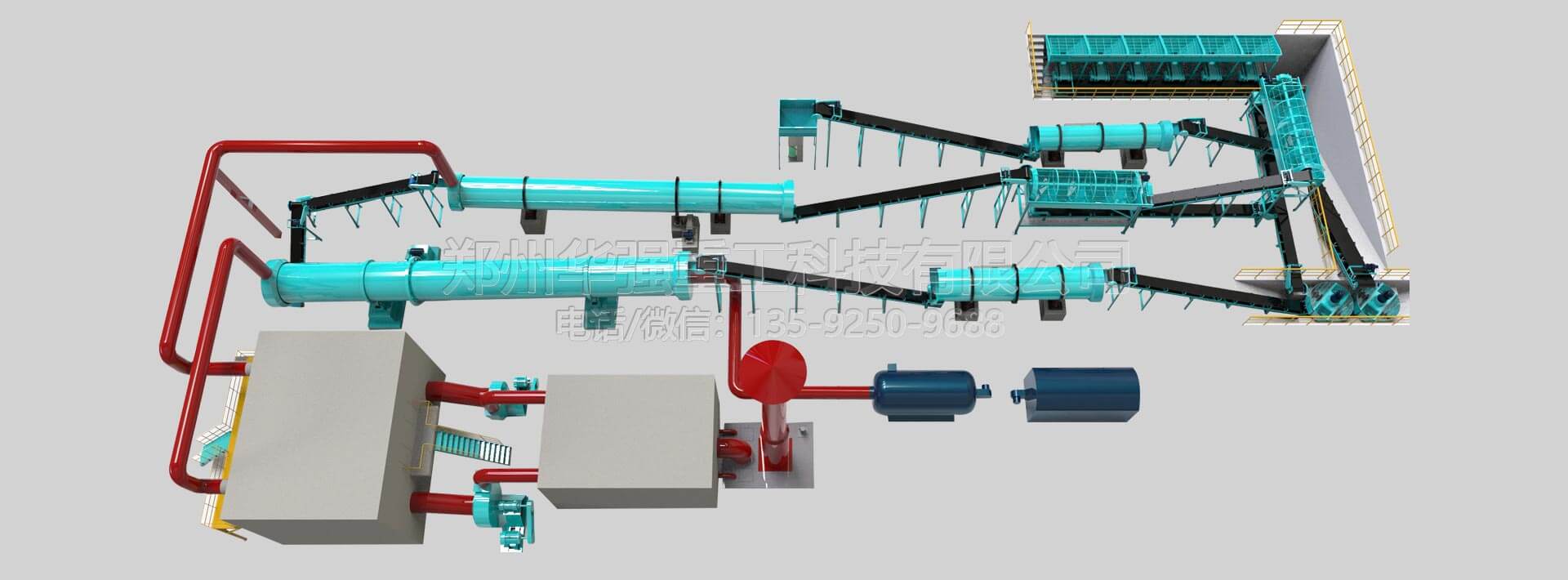
In fertilizer production lines, phosphate fertilizers are typically manufactured through acidulation of phosphate rock with sulfuric acid, creating phosphoric acid which is then processed into various phosphate fertilizers. The production involves mixing raw materials, chemical reaction, granulation, drying, cooling, and screening.
Both drum granulators and disc granulator machines can be used for phosphate fertilizer production. Drum granulators are more common for large-scale production, providing continuous operation and uniform granules. Disc granulators offer better control over particle size and are ideal for smaller batches or when frequent product changes are required.
The choice between equipment depends on production scale, desired granule characteristics, and specific phosphate fertilizer formulation requirements. Both systems can effectively handle the moist, sticky nature of phosphate fertilizer mixtures during granulation.
With global population growth and increasing food demand, phosphorus fertilizer consumption continues to rise. However, as a non-renewable resource, phosphate rock reserves are unevenly distributed globally, with about 75% concentrated in a few countries like Morocco. This resource pattern has prompted nations to emphasize efficient utilization and recycling technologies.
Scientific phosphorus fertilizer application should consider three key factors: soil test results, crop requirements, and fertilizer characteristics:
· Alkaline phosphorus fertilizers like calcium magnesium phosphate are suitable for acidic soils
· Phosphorus-deficient soils should increase basal fertilizer proportion
· High-value crops may use highly water-soluble phosphorus fertilizers
Future phosphorus fertilizer development will focus more on combining with organic fertilizers, improving utilization rates, reducing environmental risks, and achieving sustainable agriculture.