Raw Material Pretreatment: Transforming Waste into Resources
Distiller's grains (protein content 15-25%) and vinegar residue require the following pretreatment steps:
- Moisture adjustment: Reduce from 65-75% to 50-60% by adding 10-20% dry amendments (sawdust, rice husk)[1]
- pH balancing: Typically acidic (pH4.0-5.5), require 5-8% wood ash or lime to adjust to pH6.5-7.5[2]
- C/N ratio optimization: Add 15-20% livestock manure (e.g., chicken manure) to adjust C/N ratio from 30-40 to ideal 25-30 range
Core Components of Production Line
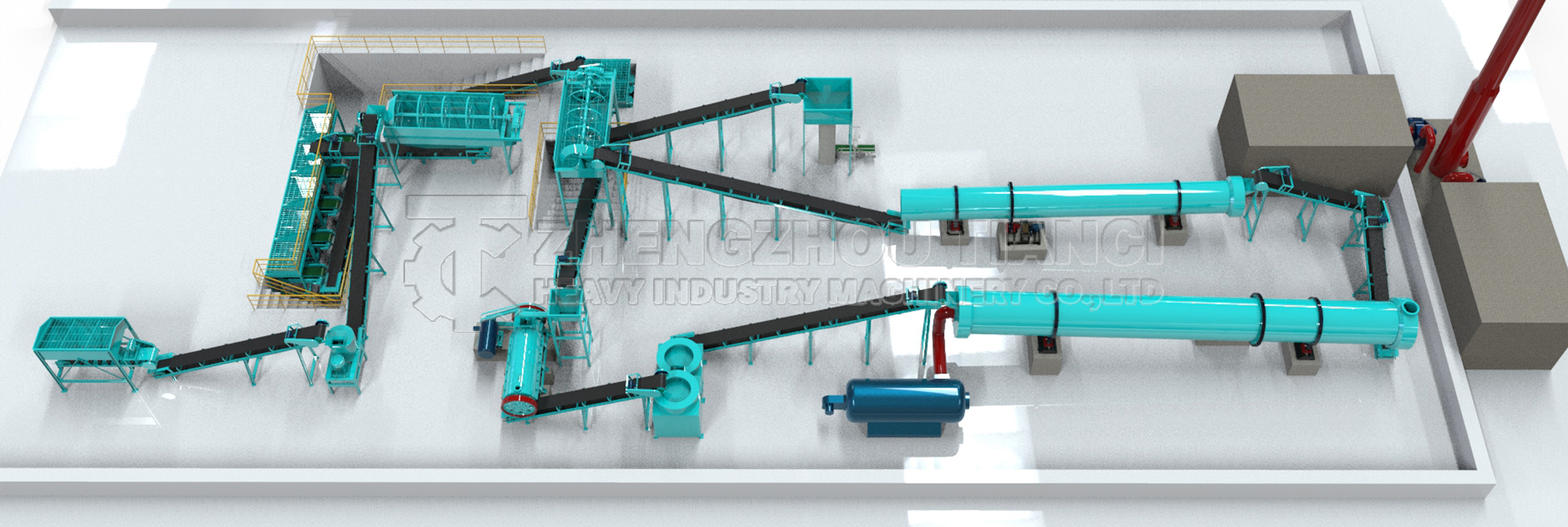
Pretreatment
Crusher
Mixer
Dewatering
Fermentation
Trough turner
Aeration system
(15-20 days)
Refining
Grinder
Screener
Dosing
Granulation
Disc granulator
Rotary drum
Post-processing
Dryer
Cooler
Packaging
Vital Role of Animal Manure
In this production process, animal manure plays irreplaceable roles:
- Nitrogen supplement: Chicken manure (N 1.5-3.5%) compensates nitrogen deficiency
- Microbial carrier: Indigenous microorganisms accelerate decomposition
- Physical improvement: Enhances pile porosity, prevents anaerobic fermentation
- Nutrition balance: Provides phosphorus, potassium lacking in distiller's grains[3]
Success Case Study
One bio-fertilizer plant uses formula: 20% distiller's grains + 30% vinegar residue + 50% chicken manure:
- Fermentation cycle shortened to 18 days (vs 25 days traditionally)
- Final product contains ≥5% NPK nutrients
- Organic matter content exceeds 45%
- Heavy metals far below national standard limits
References:
[1] "Utilization Technologies of Organic Solid Waste", China Env. Press, 2020
[2] Smith et al. "Brewery Waste Composting Optimization", Bioresource Tech, 2021
[3] FAO "Organic Fertilizer Production Guidelines", 2019 edition
